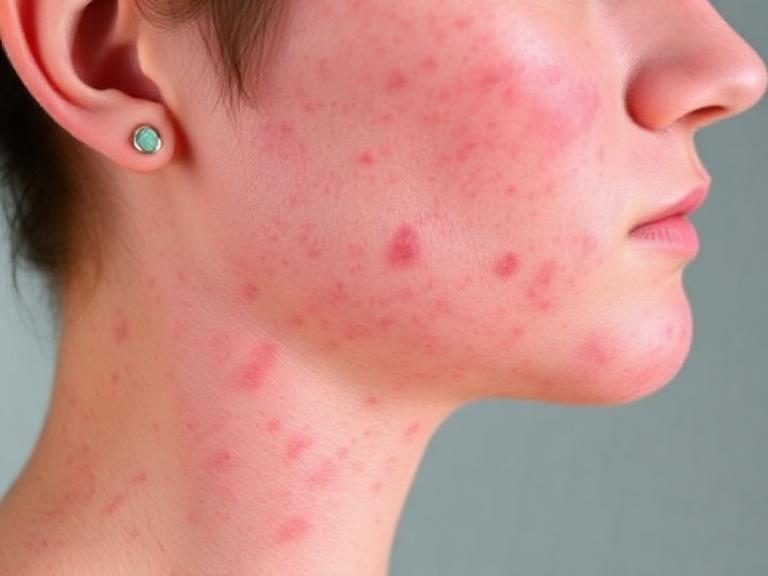
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that causes cells to build up rapidly on the skin’s surface. This buildup leads to thick, scaly patches that can itch, burn, or crack. While it’s often seen as just a skin problem, psoriasis is actually a systemic condition that can affect other parts of the body, including joints.
What Is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis happens when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, causing rapid production. Instead of shedding normally, skin cells pile up and form plaques.
Why Psoriasis Is More Than a Skin Condition
Psoriasis is associated with inflammation throughout the body and may increase the risk of conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and depression.
Who Can Develop Psoriasis?
Psoriasis can develop at any age, but it’s most common between ages 15 and 35. Both men and women are equally affected.
Types of Psoriasis
Plaque Psoriasis
The most common type—appears as raised, red patches covered with silvery scales.
Guttate Psoriasis
Characterized by small, drop-shaped spots, often triggered by infections like strep throat.
Inverse Psoriasis
Occurs in skin folds such as the underarms or groin; appears smooth, shiny, and red.
Pustular Psoriasis
Causes white, pus-filled blisters surrounded by red skin.
Erythrodermic Psoriasis
A rare but severe form that causes widespread redness and peeling.
Causes of Psoriasis
Immune System Dysfunction
Psoriasis is primarily caused by an overactive immune system that speeds up skin cell growth.
Genetic Factors
A family history of psoriasis increases risk, though not everyone with genetic markers will develop the condition.
Environmental Triggers
Psoriasis symptoms often worsen due to certain triggers.
Infections and Injuries
Strep throat, cuts, burns, or sunburns can trigger flare-ups.
Medications and Stress
Lithium, beta-blockers, and high stress levels are common triggers.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
Skin Symptoms
- Red, inflamed patches
- Silvery-white scales
- Dry, cracked skin
- Itching or burning sensation
Nail Symptoms
- Pitting
- Discoloration
- Nail separation
Scalp Psoriasis Symptoms
This can cause dandruff-like flaking, itching, and redness.
Psoriatic Arthritis
About 30% of people with psoriasis develop joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
How Psoriasis Affects the Body
Skin Cell Overproduction
In psoriasis, skin cells grow up to 10 times faster than normal.
Inflammation and Immune Overactivity
Chronic inflammation occurs throughout the body, not just the skin.
Impact on Daily Life
Severe itching, visible patches, and discomfort can affect confidence, sleep, and mental well-being.
Diagnosis of Psoriasis
Physical Examination
Doctors examine the skin, nails, and scalp for typical signs.
Skin Biopsy
A small sample may be taken to rule out other skin conditions.
Differential Diagnosis
Psoriasis can resemble eczema or fungal infections—accurate diagnosis is key.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
Topical Treatments
Steroid Creams
Reduce inflammation and slow skin cell growth.
Vitamin D Analogues
These help control rapid cell turnover.
Phototherapy
Exposure to controlled UV light slows down skin cell growth and reduces symptoms.
Oral Medications
Methotrexate
Lowers inflammation and slows skin cell production.
Cyclosporine
Suppresses the immune response.
Retinoids
Help reduce scaling and inflammation.
Biologic Treatments
Target specific immune system pathways to reduce flare-ups and inflammation.
Natural and Home Remedies
Moisturizers and Ointments
Thick creams help soothe dryness and scaling.
Aloe Vera and Coconut Oil
Provide moisture and reduce irritation.
Dead Sea Salt Baths
Help remove scales and calm the skin.
Lifestyle Management
Diet and Nutrition
Anti-inflammatory foods—like fatty fish, fruits, and vegetables—may help reduce symptoms.
Stress Reduction Techniques
Meditation, yoga, and breathing exercises help lower stress-triggered flare-ups.
Avoiding Triggers
Identify what worsens your symptoms and minimize exposure when possible.
When to See a Doctor
Signs of Severe Psoriasis
If patches spread quickly or become painful, medical care is needed.
Symptoms of Psoriatic Arthritis
Early diagnosis can prevent joint damage.
Living with Psoriasis
Emotional Well-being
Psoriasis can impact mental health—seeking support is important.
Support Groups and Resources
Connecting with others helps reduce feelings of isolation.
Skin Care Tips
Use gentle products, avoid harsh soaps, and keep skin moisturized.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition with physical and emotional impacts. While there is no cure, understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments can empower individuals to manage flare-ups effectively. With proper medical care, lifestyle adjustments, and supportive resources, people with psoriasis can lead healthy, confident lives.
FAQs
Is psoriasis contagious?
No—psoriasis is not contagious.
Can diet affect psoriasis?
Yes, certain foods may trigger flare-ups or help reduce inflammation.
Is psoriasis curable?
There is no cure, but treatments can control symptoms.
What age does psoriasis start?
It can occur at any age but is most common between 15 and 35.
Can stress make psoriasis worse?
Yes—stress is one of the leading triggers of flare-ups.