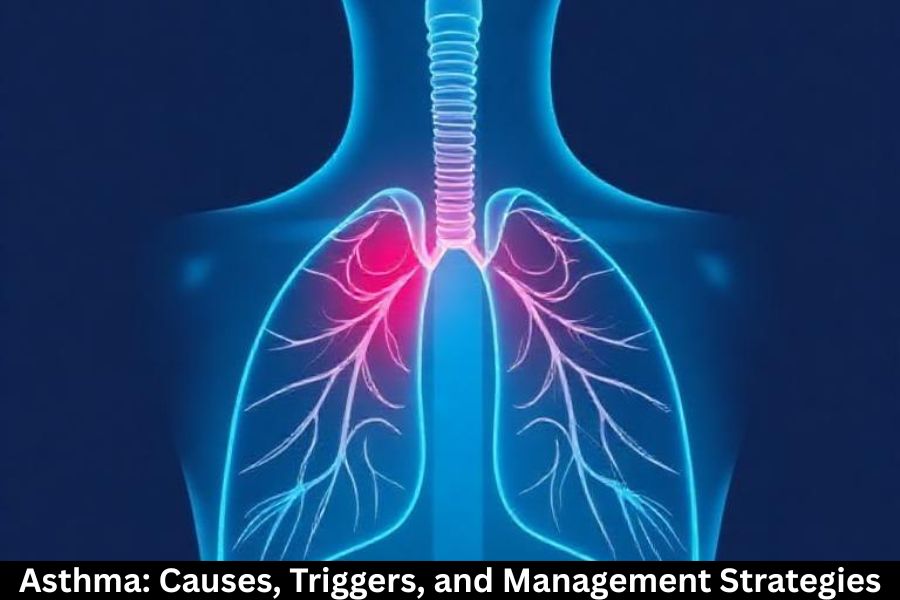
What Is Asthma?
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory condition that affects the airways, causing them to narrow and swell. This leads to symptoms like shortness of breath, wheezing, and chest tightness. Think of your airways as small pipes—when they become inflamed or clogged, airflow becomes restricted, making it harder to breathe.
How Asthma Affects the Body
During an asthma flare-up, the muscles surrounding the airways tighten, mucus production increases, and inflammation worsens. These combined effects make breathing difficult, similar to trying to inhale through a narrow straw.
Prevalence and Global Impact
Asthma affects millions of people worldwide, regardless of age. While manageable, it can significantly impact daily life if not treated properly.
Causes of Asthma
Genetic Factors
Asthma often runs in families. If one or both parents have asthma or allergies, the likelihood of developing the condition increases.
Environmental Influences
Air pollution, chemicals, cigarette smoke, and exposure to allergens at a young age can increase the risk of asthma.
Immunological Factors
Overactive immune responses, especially in early childhood, may cause the airways to become hypersensitive.
Early Childhood Exposure
Respiratory infections during infancy, such as RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus), may contribute to developing asthma later in life.
Common Triggers of Asthma
Allergens
Allergens are the most frequent asthma triggers.
Dust Mites
These tiny insects thrive in bedding, carpets, and upholstery, causing allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
Pollen
Seasonal allergies can worsen asthma symptoms, especially in spring and fall.
Pet Dander
Proteins found in pets’ skin flakes, saliva, and urine can trigger asthma.
Irritants
Smoke
Cigarette smoke—active or passive—is one of the most dangerous triggers.
Air Pollution
Industrial emissions, vehicle fumes, and household chemicals can irritate the lungs.
Weather Changes
Cold air or sudden temperature shifts often trigger symptoms.
Physical Activity
Exercise-induced asthma causes wheezing or coughing during physical activity.
Respiratory Infections
Colds, flu, and sinus infections can worsen symptoms by increasing airway inflammation.
Stress and Emotions
Strong emotions like laughter, crying, or anxiety can tighten airway muscles.
Symptoms of Asthma
Mild, Moderate, and Severe Symptoms
Asthma symptoms vary in intensity and frequency. They may include:
- Persistent coughing
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness
- Difficulty breathing
Signs of an Asthma Attack
An asthma attack is a sudden worsening of symptoms:
- Extremely rapid breathing
- Blue lips or fingernails
- Inability to speak full sentences
- Chest retractions
Diagnosis of Asthma
Medical History
Doctors examine symptoms, family history, and exposure to triggers.
Lung Function Tests
Spirometry measures how much air you can exhale and how quickly, helping confirm airflow obstruction.
Allergy Testing
Identifying allergens helps tailor treatment and avoidance strategies.
Management Strategies for Asthma
Long-Term Control Medications
These include inhaled corticosteroids and leukotriene modifiers, which reduce inflammation and prevent symptoms.
Quick-Relief Medications
Short-acting bronchodilators offer immediate relief during asthma attacks.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Avoiding Triggers
Identifying and minimizing exposure to allergens and irritants is crucial.
Home Modifications
- Using air purifiers
- Washing bedding in hot water
- Reducing humidity levels
Healthy Habits
Regular exercise, a nutritious diet, and stress management contribute to better asthma control.
Asthma Action Plans
A personalized plan outlines daily treatment, how to manage worsening symptoms, and when to seek medical help.
Natural and Home-Based Remedies
Breathing Exercises
Techniques like pursed-lip breathing and diaphragmatic breathing can help improve airflow and reduce symptoms.
Dietary Considerations
Foods rich in vitamin C, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants support lung health.
Herbal and Alternative Therapies
While some people use herbal remedies, always consult a healthcare professional before trying new treatments.
Living with Asthma
Managing Asthma in Children
Keeping track of symptoms, ensuring medication compliance, and reducing trigger exposure can help children manage asthma effectively.
Managing Asthma in Adults
Adults must balance lifestyle, stress, and environmental exposure to maintain good asthma control.
Emotional and Mental Well-Being
Anxiety and stress can worsen symptoms. Mindfulness, therapy, and support groups can help.
When to Seek Emergency Help
Warning Signs
- Severe shortness of breath
- No relief after using rescue inhaler
- Bluish skin around lips or face
Immediate Actions
Call emergency services, use quick-relief medication, and stay calm while waiting for help.
Conclusion
Asthma is a chronic condition, but with the right knowledge, treatment, and lifestyle changes, it can be managed effectively. Understanding the causes, recognizing triggers, and following a structured management plan are key to maintaining a healthy, active life. Whether dealing with mild or severe asthma, staying informed empowers you to take control of your respiratory health.
FAQs
Can asthma be cured?
Asthma cannot be cured, but it can be controlled with proper treatment.
Is asthma hereditary?
Yes, genetics play a significant role in developing asthma.
Can exercise trigger asthma?
Yes, but proper warm-ups and medications can help prevent symptoms.
What foods help asthma?
Foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3s, and vitamin C support lung function.
Can emotional stress worsen asthma?
Yes, stress can tighten airway muscles, triggering symptoms.